Introduction to Ephesus
Ephesus, one of the most well-preserved ancient cities in Turkey, stands as a testament to the grandeur and sophistication of ancient Greek and Roman civilizations. Nestled in the modern-day Izmir Province, it is a site of immense historical significance, drawing scholars and tourists alike who are eager to delve into its rich past. Known as a major trade and religious center in antiquity, Ephesus played a pivotal role in the economic and cultural exchanges that shaped the ancient world.
The city’s origins can be traced back to the 10th century BCE when it was founded by Attic and Ionian Greek colonists. As a bustling metropolis, Ephesus flourished under various rulers, including the Lydians, Persians, and eventually, Alexander the Great. However, it was during the Roman period that Ephesus reached its zenith, transforming into one of the most important cities of the Roman Empire. Its strategic location on the Aegean coast facilitated its rise as a vital hub for trade and commerce.
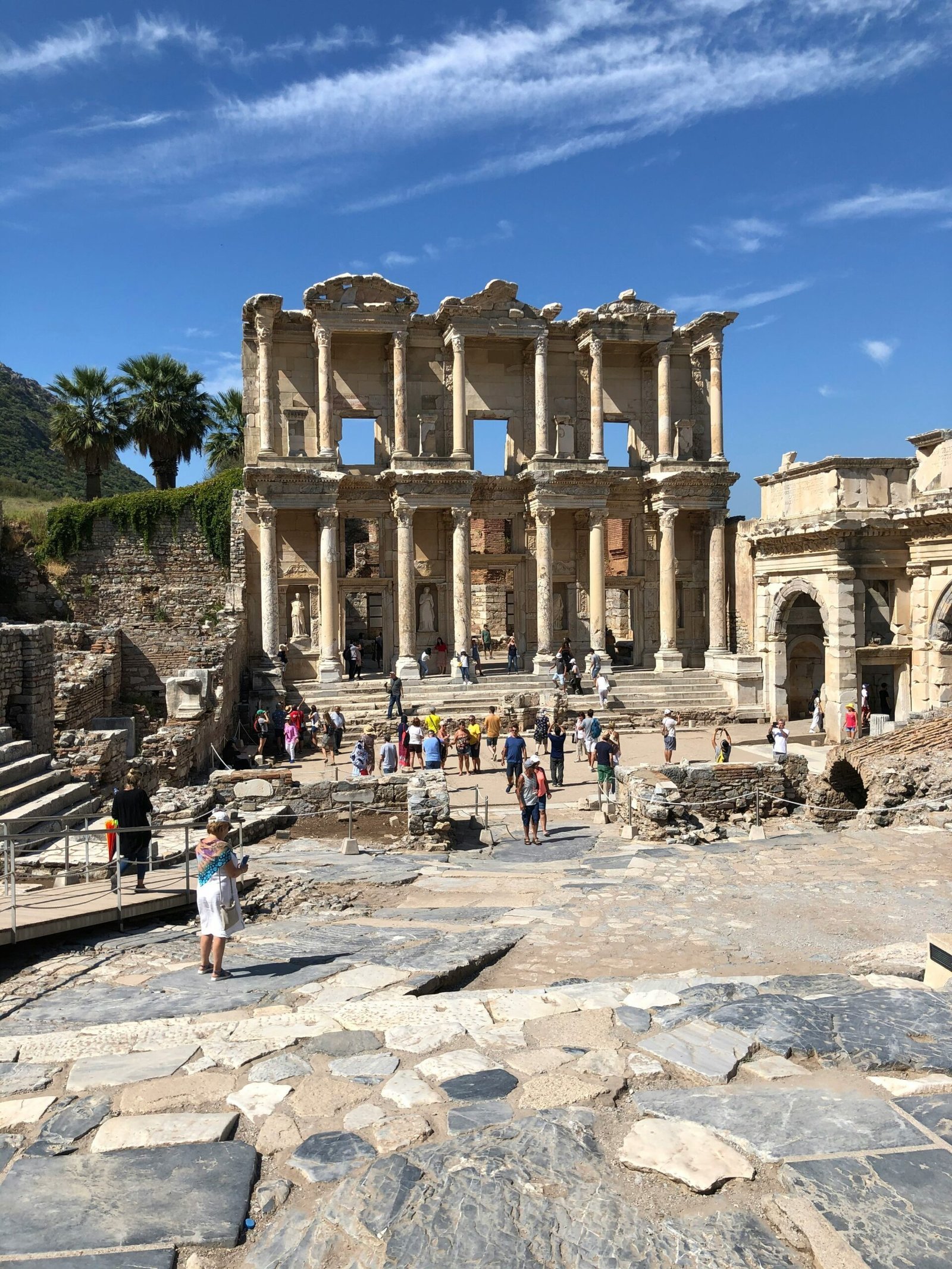
Ephesus was not only a center of commerce but also a focal point for religious activity. The Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, was located here, attracting pilgrims from across the Mediterranean. The city also holds significant Christian heritage, being mentioned in the New Testament as one of the Seven Churches of Asia and serving as a key center for early Christianity. The impressive Library of Celsus and the Great Theatre, capable of seating 25,000 spectators, further underscore the city’s historical and cultural importance.
Today, the ruins of Ephesus offer visitors a unique opportunity to walk through history, exploring the remnants of a once-thriving urban landscape. Its well-preserved structures provide a window into the architectural and societal advancements of ancient civilizations, making Ephesus a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts and casual tourists alike.
Historical Background
Ephesus, an ancient city located on the western coast of present-day Turkey, boasts a rich history that spans several millennia. Founded by Greek colonists in the 10th century BC, Ephesus quickly became an important cultural and commercial hub. The city’s strategic location near the Aegean Sea facilitated its growth and prosperity, making it a key player in the ancient world.
During the Lydian period, Ephesus saw significant development under the rule of King Croesus in the 6th century BC. The city was later conquered by the Persians, who incorporated it into their vast empire. This period of Persian dominance was marked by relative stability and infrastructural improvements, which laid the groundwork for future prosperity.
The Hellenistic era ushered in a new chapter for Ephesus, beginning with its liberation by Alexander the Great in 334 BC. Under Hellenistic influence, the city underwent substantial urban development, including the construction of grand temples, theaters, and public spaces. The cultural and intellectual vibrancy of this period attracted scholars, artists, and traders from across the Mediterranean.
Ephesus reached its zenith during the Roman period, particularly under the reign of Augustus Caesar. As the capital of the Roman province of Asia, the city flourished economically and culturally. The Romans endowed Ephesus with magnificent structures, such as the Library of Celsus and the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. These architectural marvels not only showcased the city’s wealth but also its importance as a center of learning and religion.
Key historical figures left their mark on Ephesus, contributing to its storied past. Alexander the Great’s conquest heralded a new era of growth, while Augustus Caesar’s patronage cemented the city’s status as a prominent Roman metropolis. Through these various periods of occupation, Ephesus evolved into a thriving city, rich in history and culture.
Architectural Marvels
Ephesus, an ancient city located in modern-day Turkey, is renowned for its architectural marvels that have withstood the test of time. Among its most prominent structures is the Library of Celsus, an exquisite example of Roman architecture. Built in 117 AD, this monumental edifice once held over 12,000 scrolls, serving as a grand repository of knowledge. Its facade, richly decorated with Corinthian columns and intricate reliefs, showcases the Roman penchant for grandeur and symmetry. The library’s design ingeniously incorporates a double-wall system to protect its precious contents from humidity and fire.
Another iconic structure in Ephesus is the Great Theatre, a testament to the city’s cultural and social significance. Capable of seating approximately 25,000 spectators, this amphitheater was primarily used for dramatic performances and gladiatorial contests. Its construction began in the Hellenistic period and concluded during the Roman era, reflecting a blend of Greek and Roman architectural influences. The theatre’s impressive acoustics and tiered seating arrangement highlight the advanced engineering skills of its builders.
Perhaps the most illustrious of Ephesus’s architectural wonders is the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. This grand temple, dedicated to the goddess Artemis, was completed around 550 BC. It featured 127 marble columns, each standing 60 feet tall, and was adorned with sculptural reliefs that depicted various mythological scenes. Although the temple now lies in ruins, its former grandeur continues to captivate historians and archaeologists alike.
Ongoing archaeological efforts and restorations have played a crucial role in preserving these ancient structures. Scholars and archaeologists work meticulously to uncover and restore remnants of Ephesus, providing invaluable insights into the architectural ingenuity of its past inhabitants. These endeavors ensure that future generations can appreciate the rich history and architectural splendor of this ancient city.
The Role of Ephesus in Early Christianity
Ephesus holds a pivotal place in early Christian history, underscoring its importance as more than just an ancient city. One of the most notable figures associated with Ephesus is Saint Paul, who is believed to have spent significant time there. During his stay, Saint Paul is said to have preached extensively, contributing to the spread of Christianity in the region. This is further evidenced by his writing of the Epistle to the Ephesians, a key text in the New Testament that addresses the early Christian community in Ephesus.
The city’s role in early Christianity is also highlighted by several key sites of religious significance. The Basilica of St. John, for instance, stands as a testament to the city’s rich Christian heritage. According to tradition, the basilica was built over the tomb of St. John the Apostle, making it a revered pilgrimage site for centuries. Its impressive ruins provide insight into the early Christian architecture and the reverence held for St. John among the early Christians.
Another significant site in Ephesus is the House of the Virgin Mary. Tradition holds that Mary, the mother of Jesus, spent her last years in Ephesus, taken there by St. John, as per Jesus’ instruction. The house, now a pilgrimage site, is nestled in the hills near the ancient city and is revered by both Christians and Muslims. It serves as a symbol of interfaith respect and historical continuity.
Ephesus’ contribution to the spread of Christianity is thus multifaceted, encompassing direct evangelism by early Christian figures, the creation of foundational Christian texts, and the establishment of significant religious sites. The city’s rich Christian heritage continues to draw scholars, pilgrims, and tourists, eager to explore its ancient roots and enduring legacy.
Daily Life in Ancient Ephesus
The ancient city of Ephesus, located in modern-day Turkey, was a bustling hub of commerce and daily activity. Its vibrant streets were a testament to the complex social structure and thriving economy that characterized the city. Ephesus was home to a diverse population, including merchants, artisans, and scholars, all contributing to the city’s dynamic cultural landscape.
The social structure of Ephesus was hierarchical, with the elite class enjoying a life of luxury and the common populace engaging in various trades and crafts. The economy was primarily driven by commerce, facilitated by the city’s strategic location near the Aegean Sea. Ephesus was a key trading center, attracting merchants from across the Mediterranean and beyond. Local markets were brimming with goods ranging from spices and textiles to pottery and metals, providing residents with a wide array of commodities.
Public facilities in Ephesus were advanced for their time, reflecting the city’s commitment to public welfare and hygiene. Bathhouses were a staple of daily life, serving not only as places for bathing but also as social gathering spots where citizens could relax and discuss daily affairs. The public latrines, ingeniously designed with flowing water systems, underscored the city’s emphasis on sanitation and community health.
Residential areas in Ephesus varied significantly, with the affluent living in lavish homes adorned with intricate mosaics and frescoes, while the lower classes resided in more modest dwellings. Despite these differences, the sense of community was strong, with neighbors often engaging in social and cultural activities together.
Cultural practices in Ephesus were rich and varied, deeply influenced by Greek and Roman traditions. Festivals, theatrical performances, and religious ceremonies were integral parts of Ephesian life, providing entertainment and spiritual fulfillment to its residents. The city’s renowned Library of Celsus and the Great Theatre were central to its cultural identity, showcasing the intellectual and artistic achievements of its people.
In essence, daily life in ancient Ephesus was a blend of commerce, culture, and community, making it one of the most fascinating cities of the ancient world.
Modern-Day Ephesus: Tourism and Preservation
Today, Ephesus stands as a testament to the grandeur of ancient civilizations, attracting scholars, historians, and tourists from around the globe. The Turkish authorities, in collaboration with international organizations such as UNESCO, have undertaken extensive efforts to preserve and present the ancient ruins in their utmost authenticity. This meticulous preservation work ensures that visitors can experience the city’s historical significance while safeguarding its integrity for future generations.
Visitors to Ephesus can embark on guided tours that provide a comprehensive overview of the site’s rich history. Professional guides lead these tours, offering in-depth insights into key attractions such as the Library of Celsus, the Great Theatre, and the Temple of Artemis. These iconic landmarks, meticulously restored, give a glimpse into the architectural and cultural marvels of the ancient world.
The visitor facilities at Ephesus are designed to enhance the overall experience while ensuring the preservation of the site. Modern amenities such as information centers, rest areas, and designated pathways help manage the flow of tourists, minimizing impact on the delicate ruins. Additionally, educational exhibits and interactive displays provide deeper understanding and engagement, making the visit both informative and enjoyable.
Preservation efforts at Ephesus face several challenges, primarily due to natural and human-induced factors. The site’s exposure to environmental elements, including weathering and seismic activity, poses significant risks. Moreover, the increasing number of visitors each year necessitates stringent management practices to prevent wear and tear. Turkish authorities, supported by international experts, continuously monitor and implement conservation strategies to address these challenges, ensuring the site remains protected.
In conclusion, Ephesus stands as a remarkable example of ancient heritage preserved amidst modern-day challenges. Through concerted efforts by local and global entities, the city’s historical treasures are maintained, allowing visitors to delve into its rich past while safeguarding it for future generations.
Tips for Visiting Ephesus
When planning a visit to the ancient city of Ephesus in Turkey, certain practical considerations can greatly enhance your experience. To begin with, the best times to visit Ephesus are during the spring (April to June) and autumn (September to October) seasons. The weather during these periods is mild and pleasant, allowing for a comfortable exploration of the ruins without the intense summer heat.
Getting to Ephesus is relatively straightforward. The nearest airport is in Izmir, located about 60 kilometers away. From Izmir, you can take a shuttle bus, a private taxi, or rent a car to reach the ancient site. Additionally, regular buses and trains connect Izmir to the town of Selçuk, which is situated just a few kilometers from Ephesus. From Selçuk, local minibusses or taxis can take you directly to the entrance of the archaeological site.
The entrance fee to Ephesus is around 200 Turkish Lira, though prices can vary slightly depending on the season and any additional exhibits you might wish to visit, such as the Terrace Houses. It’s advisable to bring cash for entrance fees, as card payment options may not always be available.
To ensure a comfortable visit, it is recommended to wear sturdy walking shoes, as the terrain can be uneven. Bringing a hat, sunscreen, and plenty of water is essential, especially during warmer months. A camera or smartphone will help capture the remarkable history and beauty of the site, but remember to carry a small backpack for convenience.
For accommodations, the town of Selçuk offers a range of options from budget-friendly hostels to more luxurious hotels. Some popular choices include Hotel Bella, Ayasoluk Hotel, and Cella Boutique Hotel & Spa. Dining options are also plentiful in Selçuk, with local restaurants offering Turkish cuisine. Artemis Restaurant and Ejder Restaurant are highly recommended for a delightful dining experience.
If you are on a tight schedule, a day trip to Ephesus is feasible, covering major highlights like the Library of Celsus, the Great Theatre, and the Temple of Artemis. However, for a more in-depth exploration, a two-day itinerary allows you to fully appreciate the site and visit nearby attractions such as the House of Virgin Mary and the Ephesus Museum in Selçuk.
Conclusion: The Timeless Allure of Ephesus
Ephesus stands as a monumental testament to the grandeur and sophistication of ancient civilizations. As a travel destination, it offers an unparalleled window into the rich tapestry of history, allowing visitors to traverse through time. The city’s blend of meticulously preserved ruins, such as the Library of Celsus and the Great Theatre, alongside the remnants of daily life, provides a vivid portrayal of a society that once thrived in intellectual and cultural pursuits.
The enduring legacy of Ephesus is palpable, not just in its physical structures but also in its influence on modern culture and tourism. The ancient city continues to captivate the imagination of historians, archaeologists, and tourists alike. Its streets, once walked by notable figures such as Heraclitus and Saint Paul, echo with stories that have shaped the fabric of human history. Ephesus is more than just a historical site; it is a living museum where each stone tells a story, and every corner reveals a piece of the past.
Modern visitors can immerse themselves in the architectural marvels that have stood the test of time, from the grandeur of the Temple of Artemis to the intricate mosaics of the Terrace Houses. The cultural significance of Ephesus extends beyond its ruins, offering a profound connection to the ancient world and its myriad contributions to art, philosophy, and governance. Experiencing Ephesus firsthand allows one to appreciate the ingenuity and spirit of a civilization that continues to inspire awe and wonder.
In essence, Ephesus is a beacon of historical and cultural richness that beckons travelers to explore its timeless allure. Whether you are a history enthusiast, a lover of architecture, or simply someone seeking to connect with humanity’s past, Ephesus promises an unforgettable journey. Embrace the magic of Ephesus and let its ancient splendor leave an indelible mark on your travel experiences.